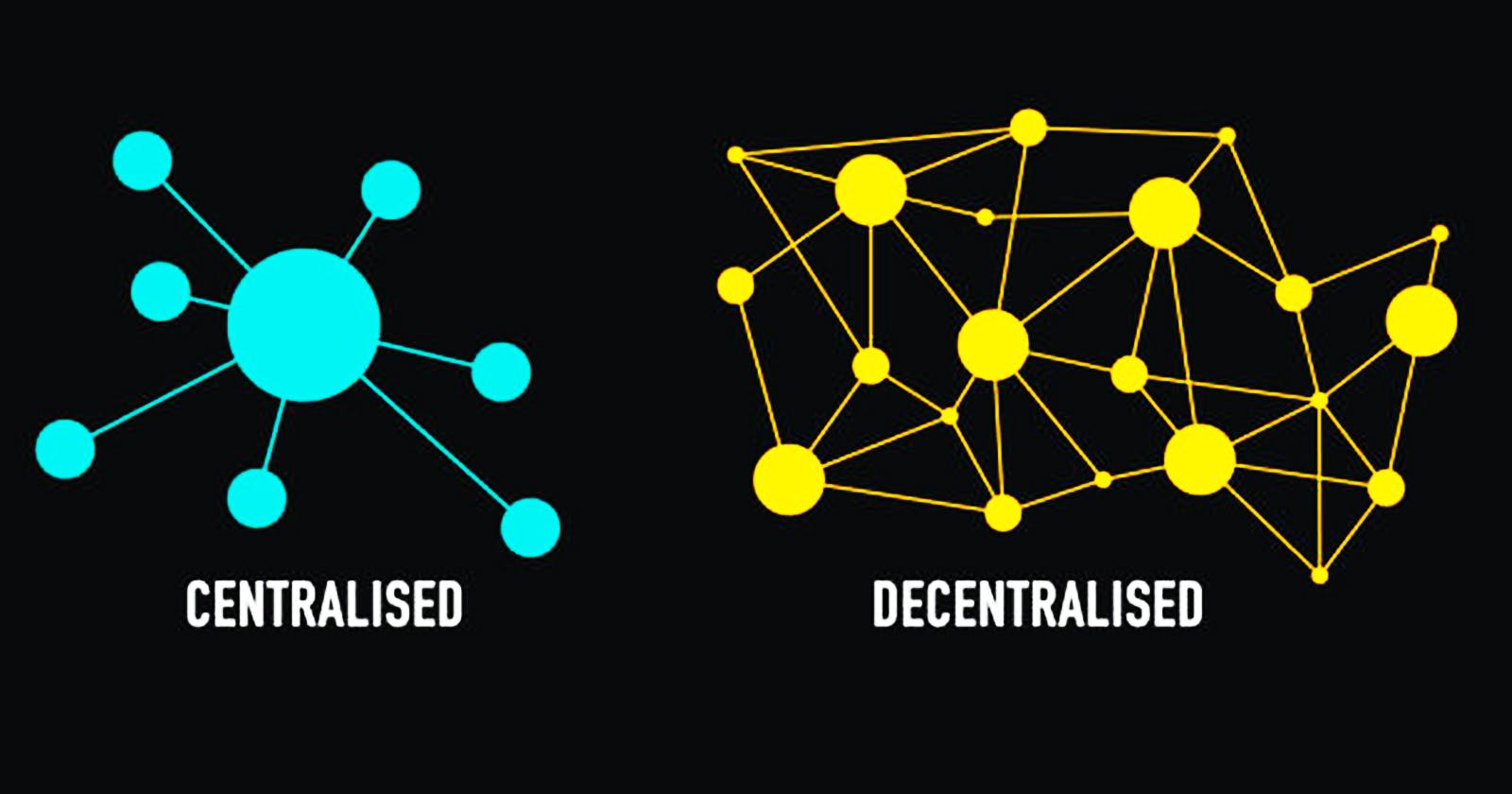
What it Means
In blockchain, decentralization refers to the transfer of control and decision-making from a centralized entity (individual, organization, or group thereof) to a distributed network.
Example:
Imagine a group of friends planning a picnic in the park.They decide to decentralize the planning process. Each friend is now responsible for bringing something to eat, deciding on a game to play, or suggesting a spot in the park.
As a result, the picnic becomes more diverse and enjoyable. The workload is shared, making the planning process smoother ,An example of decentralization (Distribution of work)
Decentralization in Blockchain: Why It Matters
In the blockchain technology, decentralization reigns supreme as a defining feature with profound implications. But what exactly makes decentralization so crucial in the context of blockchain? Let's know the reasons why decentralization matters and its impact on the world of digital currencies and beyond.
[1] Preserving Trust and Integrity
At the heart of decentralization in blockchain lies the preservation of trust and integrity. Traditional financial systems rely on centralized authorities such as banks to verify transactions and maintain records. However, this centralized model is susceptible to corruption, manipulation, and single points of failure. Decentralization eliminates the need for middle man by distributing transaction validation across a network of nodes. This ensures transparency and trustworthiness, making it virtually impossible for any single entity to tamper with the integrity of the blockchain.
[2] Upholding Privacy and Security
Decentralization in blockchain offers enhanced privacy and security by design. Unlike centralized databases where sensitive information is stored in a single location, blockchain distributes data across multiple nodes, making it resistant to hacking and unauthorized access. Moreover, blockchain's cryptographic algorithms ensure that transactions are pseudonymous and immutable, protecting users' privacy and preventing censorship. This level of privacy and security is especially critical in an era of increasing digital surveillance and data breaches.
[3] Optimizes resource distribution
Decentralization can also help optimize the distribution of resources so that promised services are provided with better performance and consistency, as well as a reduced likelihood of catastrophic failure.